Setting the right product price in a print-on-demand business shapes store performance and overall profitability.
A well-planned pricing strategy considers production cost, market competition, and consumer demand while ensuring a sustainable pricing model that aligns with business goals.
Whether selling t-shirts or other custom apparel, evaluating pricing tiers and profit margins is essential to optimize revenue generation.
A competitive pricing structure must incorporate cost analysis, value-based pricing, and pricing psychology to enhance sales conversion.
The online store’s pricing framework should also factor in demand forecasting and price elasticity to maintain affordability while maximizing revenue streams.
With a strong approach to pricing optimization, businesses can position their products effectively in the marketplace, ensuring financial planning supports long-term growth.
Pricing transparency and pricing experiments help refine the selling price, allowing brands to stay ahead in the POD industry while balancing pricing competitiveness and customer retention.
Table of Contents
ToggleSteps 1: Define Your Product’s Cost

The significant need of the cost of the product is the growth of the business.
Once you can define the cost you are ready to define the market segment and to shape the competition in the market.
You need to keep an eye on the price of competitors and the demand of the market segment to excel in the business line.
You have clear strategy over cost and expenditures irrespective of the fact involved in selling print on demand or drop shipping the product.
Design Costs
Pricing for design services require a strategic approach, whether outsourcing to a designer or creating your own artwork.
The design price calculation should account for every product item sold to maintain a strong profit margin.
Design price / number of designs you plan to sell = design cost per product
If producing in limited volume or offering a limited-time offer, setting a chosen price that covers the design cost per product is essential.
Tools like Printout’s Design Maker can minimize expenses, but factoring in valuable time spent ensures fair compensation.
Establishing a realistic hourly rate based on hours spent provides clarity on the true product cost, while adjusting pricing according to projected units sold helps achieve a break-even point.
Design price / your profit margin = minimum orders to sell
A well-structured retail price and careful adjustments to minimum orders can drive effectiveness, making working on your business both profitable and sustainable.
Your hourly rate x hours spent on the design = design price
Product Cost
Understanding production cost is essential when pricing print-on-demand services, as every item you sell already includes this expense.
Whether you’re browsing Printful’s product prices on their Product page or adding products to your store, factoring in these costs ensures you set a price that maintains profitability.
The process of integrating these numbers into your pricing strategy is crucial, and analyzing them thoroughly before finalizing a price helps avoid unnecessary losses.
Watching a video tutorial or reviewing pricing structures within your platform can provide further clarity on balancing costs and profit margins effectively.
Shipping Cost
Setting the right pricing strategy for print-on-demand products requires a careful balance between affordability and profitability, especially when considering shipping expenses.
Many online businesses struggle with cost-effective shipping while maintaining a competitive edge in the ecommerce industry.
Factoring in order fulfillment, logistics, and delivery speed is crucial to ensuring customer satisfaction and boosting conversion rates.
A well-structured pricing framework integrates shipping costs seamlessly into the final price, preventing cart abandonment and enhancing consumer trust.
Businesses often opt for free shipping thresholds to encourage higher cart value, leveraging purchase triggers to drive repeat customers and optimize revenue generation.
Transparent pricing appeals to buyers, fostering consumer confidence and increasing average order value.
The impact of shipping promotions on purchasing trends highlights the significance of perceived affordability in pricing competitiveness.
Strategic pricing should incorporate direct costs and pricing flexibility to align with market demand, ensuring cost efficiency while sustaining ecommerce profitability.
By analyzing cost structure and pricing accuracy, businesses can maximize profit potential without compromising customer loyalty.
The ability to navigate price sensitivity and pricing perception influences online sales, emphasizing the importance of demand forecasting and cost consideration.
Checkout incentives, such as promotional discounts, can significantly enhance customer decision-making, reinforcing pricing effectiveness and business growth.
Brands that focus on price competitiveness and product positioning achieve greater success in the digital marketplace, driving ecommerce revenue and long-term profitability.
Taxes
When setting the price for your print on demand products, it’s essential to consider taxes, which can vary significantly based on your customer’s location.
For example, in the United States and Canada, sales tax is typically charged on orders, while in regions like the EU, UK, Norway, and Liechtenstein, VAT is applicable.
Meanwhile, GST applies in countries like Australia and New Zealand. Your responsibility could also extend to collecting tax from customers, depending on local regulations.
The tax rate can fluctuate between 4% to 10% in the US and 17% to 27% in the European Union, with different base prices impacting the final amount charged.
The exact percentage depends on where your customer is located, which makes it tricky to predict the rate in advance.
As a result, it’s advisable to consult a tax specialist to navigate the nuances of these taxes.
Understanding these variations can help you accurately factor taxes into your product price and avoid any surprises in the final amount.
Platform Fee Per Order
When pricing your print on demand products, it’s crucial to factor in the fees that platforms like Shopify, Etsy, and eBay may charge for hosting your online store and processing your sales.
Some platforms require a fixed cost, while others, such as Etsy or eBay, may take a percentage of each sale and charge a separate listing fee.
Payment processors like PayPal might also charge a transaction fee, although they are typically free to set up.
Being aware of all these costs and adding them to your product pricing is key to maintaining profitability.
These platform fees can have a significant impact on your final price, so it’s important to keep them in mind when deciding how much to charge your customers.
Step 2: Add A Profit Margin

Once you have calculated your product costs, the next step is to factor in a profit margin to determine the retail price.
This is your opportunity to get creative and play with different pricing strategies.
By adjusting the margin, you can ensure that your price remains competitive with other sellers while also positioning your product in the right price range within the market.
Product cost + profit margin = retail price
Keep in mind that your price should be within an acceptable range compared to competitors; pricing too high may make it difficult to make a sale, while pricing too low might not cover the effort and time you’ve invested in running your store.
It’s essential to consider the work involved in your store management, especially when you’re putting in long hours.
For instance, if you choose a 20% profit margin, make sure it covers your other costs and supports your efforts effectively.
Step 3: Add Other Cost
To accurately price your print on demand products, you’ll need to consider all costs involved in running an online store, not just the direct product price.
Fixed costs like monthly ecommerce platform subscriptions, advertising budget, and services such as your internet bill, can add up quickly.
Once you’ve accounted for these expenses, it’s important to balance them against your profit margin to ensure profitability.
By dividing your monthly expenses by the profit margin, you can calculate how many products you need to sell to break even.
If your minimum orders or retail price seems unrealistic, it’s time to adjust your expenses and balance your budget accordingly.
Step Four: Review Your Prices Regularly
In this most important step is to consistent review of the pricing strategy of the product.
The need to continuous change in price is to update the pricing strategy to meet up the expenses.
Following are some important considerations during the process:
1. Market Or Competition-Oriented Pricing
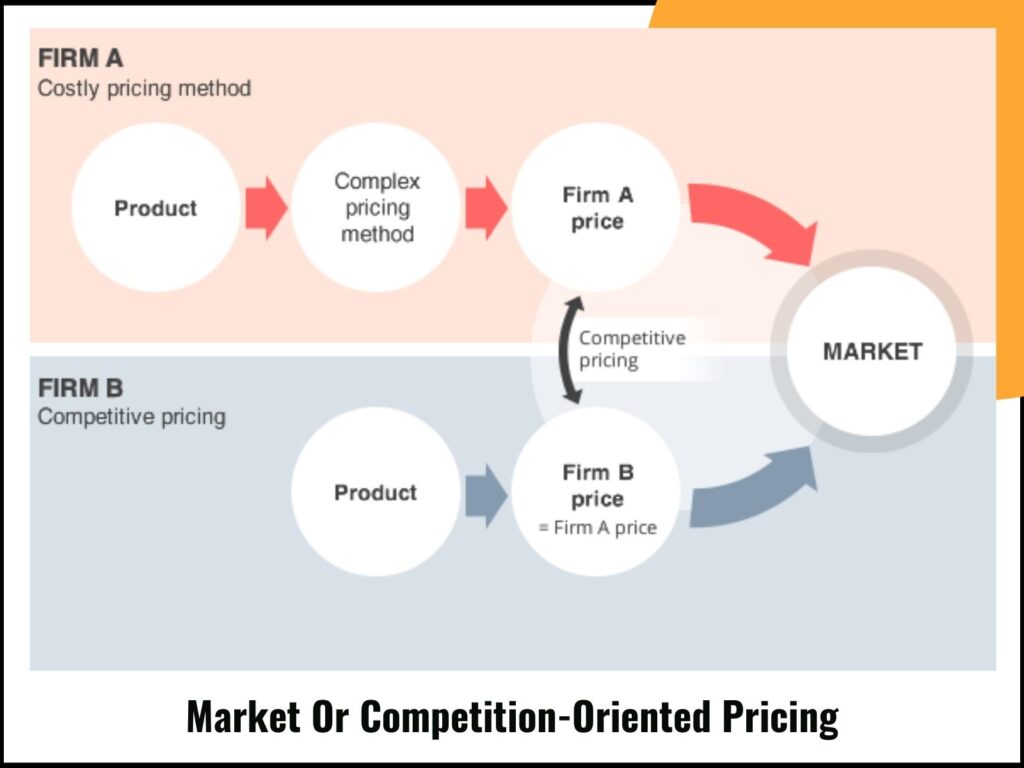
To effectively price your print-on-demand products, it’s crucial to assess the market and your competitors.
Start by researching the average price range of similar products to ensure your pricing remains competitive and within an acceptable range.
There are a few strategies to consider when pricing—one is to offer added value such as personalized messages or better visual presentation, which can justify a higher price.
Alternatively, you could price your items similarly to your competitors to appeal to a broader audience without straying too far from the market average.
If you’re looking to steal customers from your competition, pricing slightly below the market average could work, but be cautious.
Underpricing may seem appealing, yet it can result in failing to cover your costs, and may even raise doubts about your product’s quality.
Pricing Above The Market Average
When you choose to price your print-on-demand products above the market average, you’re aiming to distinguish yourself from competitors by offering added value.
This can be achieved by enhancing the shopping experience, such as including free gifts, offering personalized messages, or using high-quality visual elements like professional photos and a sleek store design.
This strategy positions your product as premium, appealing to customers who are willing to pay a little extra for unique or high-quality offerings.
However, it’s important to ensure that the perceived value matches the higher price point, as otherwise, customers may hesitate to make a purchase.
Pricing The Same As The Market
Pricing your products the same as the market average is a safe approach, especially if your goal is to target a wide audience and remain competitive.
By matching your competitors’ prices, you eliminate the risk of being too high or too low, which could either turn potential buyers away or make it hard to cover your costs.
This pricing strategy appeals to customers who are looking for a familiar product at a reasonable cost, and it enables you to fit within the same price range as your competition, thus attracting similar customer groups.
While this approach ensures consistent sales, you’ll need to ensure that your value proposition stands out in other ways, such as through marketing, customer service, or product variety.
Pricing Below The Market Average
Pricing below the market average can be an effective strategy for attracting customers who are drawn to deals or lower prices, potentially undercutting your competitors and gaining their customers.
By pricing your products more affordably, you can appeal to cost-conscious buyers.
However, this comes with risks—severely underpricing a product may not allow you to cover your costs and could even make your product appear inferior or “sketchy” to some customers.
It’s crucial to balance the appeal of a lower price with the need to maintain a quality perception.
This approach can help you stand out in a crowded market, but it requires careful consideration of costs and customer expectations to avoid financial strain.
2. Demand / Dynamic Pricing
To effectively price print on demand products, it’s crucial to stay updated on market trends and customer desires.
Dynamic pricing enables you to adjust product prices based on demand and seasonality. For instance, you can raise prices for seasonal products like hoodies and beanies during fall and winter, when demand is higher, and lower them during the summer months when demand tends to drop.
Monitoring demand fluctuations and market forces allows you to fine-tune pricing strategy and stay competitive.
By constantly adjusting your prices based on seasonal adjustments and buyer behavior, you can make the most of each season’s sales opportunities.
Pricing flexibility is essential to align with changes in demand and to cater to your customers’ needs effectively, without losing sight of the overall market pricing trends.
3. Anchor Pricing
Anchor pricing is a clever strategy many brands use to increase sales and attract customers.
By establishing a higher imaginary price and then offering a lower discount price, the product seems like a steal, creating an appealing deal for bargain hunters browsing the internet.
This pricing tactic plays on consumer psychology, as the perceived value of a product rises when the discount seems significant.
It also taps into the idea of price comparison, where customers feel they are getting a great deal.
While effective, anchor pricing needs to be handled carefully to avoid manipulation accusations.
Properly executed, it can influence consumer behavior, boost sales, and enhance your brand’s marketing appeal, making your products stand out in a competitive market.
4. Discount Pricing
When implementing discount pricing, it’s important to consider both the current market price and your sales strategy.
By setting a starting price that’s higher than the market average, you can create the potential for future discounts and promotions, drawing in bargain shoppers, especially during popular ecommerce events like Black Friday or Cyber Monday.
This approach often leads to bursts of sales as customers are drawn in by appealing deals.
It’s crucial to leave room for discounts in your pricing strategy to ensure that, when sales do occur, they don’t negatively impact your ability to cover expenses.
A well-executed discount offer can attract more customers while maintaining healthy margins if managed with the right expectations and pricing flexibility.
Just remember that your store’s promotional pricing and markdowns need to align with consumer behavior and ensure they feel like a genuine deal.
5. Penetration Pricing
When entering a competitive market, employing penetration pricing can be an effective strategy, particularly when aiming to attract a large customer base.
By setting a price below the market average initially, you can draw in potential customers, and over time, as customer loyalty increases, you have the flexibility to gradually raise the price.
This approach is often seen in startup companies that grow into market leaders, like Netflix. However, don’t make the mistake of leaving your prices static.
As demand fluctuates, product costs rise or fall, and market conditions shift, your retail price should adapt to reflect these changes.
Staying flexible with your pricing allows you to maintain your position in the market and continue attracting loyal customers, while also ensuring your business grows sustainably.
Example: Pricing A Printful T-Shirt
When pricing a Printful t-shirt for your Shopify store, the process starts with creating a detailed cost assessment to determine the most accurate price.
By using an excel sheet, you can easily track all the variables involved, from the product costs to pricing adjustments.
Although the costs mentioned might change over time, it’s crucial to follow along with the steps in the pricing process to calculate the final amount accurately.
As a basis, research is key to keeping your store’s pricing competitive, ensuring it aligns with your target market.
This example of product pricing for a classic t-shirt allows you to see how to create your pricing strategy and pricing method, making adjustments as you go, depending on your research and evolving costs.
Step 1: Assessment Of Product Cost

When pricing print on demand products, it’s crucial to assess all related costs right from the start.
This includes design costs, which can be calculated by multiplying your hourly rate by the time spent creating the design.
For example, if you’re designing a Printful shirt, consider not only your hourly rate but also the number of designs you plan to sell to divide the design cost per product.
Your hourly rate x hours spent on the design = design price
My hourly rate will be $45/hour and I’m going to multiply that by the time I spend on my design, which is 1/6 of an hour. That’s $7.50 for this design.
Design price / number of designs you plan to sell = design cost per product
Next, calculate your production costs based on factors like product color, size, print placement, and the fulfillment location.
Make sure to use tools like Printful’s price calculator to get the most accurate cost for each item, as prices can vary depending on the product specifics.
When pricing products in different sizes, you have several methods to choose from based on your pricing strategy:
Price Each Size Separately
You can treat each size as a distinct product, which means a design might cost $14.98 for sizes XS to XL, but $16.43 for size 2XL. This creates a different retail price for each size, which can lead to inconsistencies in pricing and may not always be ideal for your sales strategy.
Price By The Most Expensive Size
This approach sets the cost based on the most expensive size, which in this case is $16.43 for 2XL. If a customer buys a smaller size like XS to XL, you make an extra $1.45 in profit. However, if they buy a 2XL, you break even. This works well if you’re not trying to keep retail prices as low as possible but are instead aiming for a balanced margin across sizes.
Price By The Less Expensive Size
If you want to keep prices consistent across all sizes, you could price based on the less expensive size, like XS to XL, at $14.98. However, if a customer buys the 2XL, you’ll incur a $1.45 loss, which reduces your profit margin. This approach helps keep the price low for customers but can affect your overall profitability.
Calculate The Average Cost
Another option is to average the prices across all sizes. For example, the average cost of $15.22 would be the sum of all sizes’ costs divided by the number of sizes. In this case, for every XS to XL sold, you’d gain 24¢ to offset the $1.21 loss on each 2XL. This method smooths out the cost differences across sizes, ensuring a more consistent price but still accounting for varying costs.
Add shipping costs to the equation, especially if you plan to offer free shipping to customers in the USA, as this can affect your retail price.
Your retail price + printful’s shipping rate = your retail price with free shipping
Additionally, remember to factor in platform fees from services like Shopify, including transaction fees and order processing fees.
To ensure you’re on track, always account for taxes, which will depend on the location where you’re selling, as well as any applicable sales tax.
By strategically analyzing these factors, you can determine your product price, making necessary adjustments to maintain profitability while staying competitive.
COST SUMMARY

The production cost comes to $15.22, shipping adds $3.99, taxes are $1.39, and Shopify charges 30¢ plus 2.9% of the retail price.
This brings the total cost to $20.90 plus 2.9% of your retail price.
Step Two: Add A Profit Margin
Product cost + profit margin = retail price
Now, it’s time to factor in a profit margin. Let’s add 20% to the product cost:
$20.90 + 20% = $25.08. Rounding that up gives us a retail price of $26.
However, we need to account for Shopify’s 2.9% fee on the retail price, which equals 75¢. This brings our new cost to $21.65, and our profit margin is now $4.33.
Step Three: Add Up Other Costs
Now, let’s factor in additional monthly costs. My Shopify Basic subscription costs $29 a month.
I also purchased a domain from Domain.com for $9.99 annually, which breaks down to 83¢ per month. Don’t forget the $7.50 design cost.
Other monthly costs / your profit margin = minimum orders per month
Adding up my monthly expenses ($37.33) and dividing by my profit margin ($4.33), I need to sell at least 8-9 designs per month to cover costs. If I want to start profiting, I’ll need to sell more.
Keep in mind that product costs will vary depending on factors like customer location and taxes.
Pricing might need to be adjusted based on market trends, competition, or seasonality.
It’s important to regularly revisit your pricing strategy, adjust costs when needed, and try new approaches to keep the business thriving.
Conclusion
To properly price your print-on-demand products, always ensure that you factor in your product costs, which can vary based on production technique, fulfillment location, shipping costs, and taxes.
You need to assess the cost breakdown, including your design costs and platform fees, to establish a solid pricing strategy.
Pricing models like cost-based or competitive pricing can guide your decisions, but always adjust your profit margins according to market demand and your competitors’ pricing.
Keep an eye on any price fluctuations due to transaction fees, shipping rates, and size differences in your product categories.
Regularly reviewing your pricing structure helps you stay competitive and ensures that your business can cover the break-even point and generate consistent profit.
Tracking your profit margins closely allows you to make any necessary price adjustments and fine-tune your pricing formula for better customer engagement and long-term success.
FAQs
Q1: How do I determine the retail price for my print-on-demand products?
The retail price should be the sum of your product costs (including production, shipping, taxes, and platform fees) plus your desired profit margin. You can adjust your profit margin based on competition and market demand.
Q2: What factors should I consider when setting the price for different product sizes?
Consider the production costs for each size, as larger sizes may incur higher production and shipping costs. You can either price each size individually, calculate based on the most expensive size, or average the cost across all sizes.
Q3: How can I ensure my print-on-demand prices remain competitive?
Monitor your competitors’ pricing regularly, adjust based on market trends, and offer value through unique designs or free shipping. You can also experiment with pricing methods like dynamic pricing to stay competitive.
Q4: What are the key costs involved in pricing print-on-demand products?
Your key costs include production costs, shipping fees, taxes, platform fees, transaction fees, and any design costs. Factor all of these into your price calculation to ensure profitability.
Q5: Should I include taxes in my retail price?
Taxes, such as sales tax, should be accounted for separately from your base product price. In some cases, you may need to include them in the final retail price, depending on the region you’re selling in and local tax laws.
Q6: How do shipping costs affect my product pricing?
Shipping costs vary depending on the customer’s location, and this needs to be factored into your price. You can either include shipping costs in the product price or offer free shipping by adjusting your pricing strategy.
Q7: What is the break-even point, and how does it impact my pricing strategy?
The break-even point is the number of products you need to sell to cover all your fixed and variable costs. It’s crucial to know this to set pricing that not only covers your expenses but also generates a profit.




















